Product-led growth (PLG) is a popular go-to-market strategy, especially among B2B SaaS companies. The approach leverages the product itself as the primary driver of customer acquisition, expansion, and retention.
This guide will help you learn how you can implement a PLG funnel into your sales and marketing strategies to use your product itself to drive customer acquisition.
Specifically, we will differentiate between the sales funnel strategies for small and medium-sized businesses (SMB) and enterprise businesses.
What does PLG stand for?
Firstly, what does PLG stand for in business? PLG stands for “Product-Led Growth.” It’s a business growth strategy that leverages product usage as the primary driver to acquire, retain, and expand customers.
To clarify the Product-Led Growth model further, let’s compare it with two other prominent business growth strategies:
- Marketing-Led Growth: This strategy emphasizes marketing activities to generate inbound leads, thereby initiating the sales funnel.
- Sales-Led Growth: This approach places sales activities at the forefront, driving outbound sales campaigns and setting the sales funnel in motion.
Product-led growth, conversely, gets ahead of these two activities and puts the product in front. Why?
The person who buys your product will learn a lot about it. If your product really speaks to them, congratulations! You’ve found a way to grow that can be scaled up. Not sure what it means when it says “If your product directly speaks to the end-user”? Let’s take it apart.
Product-Led Growth (PLG) is a business strategy that puts your product in the lead when it comes to gaining new customers. It uses the product’s features and user experiences to connect with and engage users, so they don’t need a salesperson or any other help. In a sense, the product does both marketing and selling.
What is a Product-led Growth Funnel?
Understanding the concept more clearly, you might have an idea now, more or less. Let’s take an actionable step to learn how to create a PLG sales funnel that generates a pipeline.
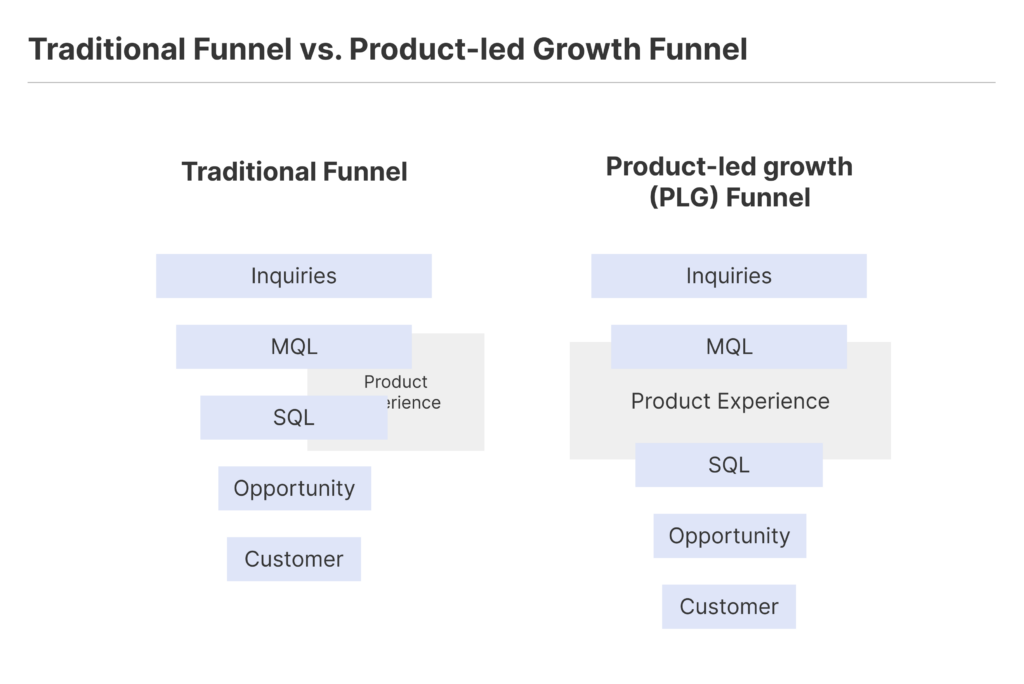
In traditional sales funnels, the experience of using the product is often less important at each stage. On the other hand, the PLG funnel puts the most importance on the product experience, which drives the whole sales pipeline by using your product’s strengths.
The PLG sales funnel is a model for getting new users and making more money by putting the focus on the user experience of the product. Here, the focus is on making a product that gives users an experience that makes them happy and keeps them coming back.
Also, putting the focus on the product experience at different points in the funnel makes sure that leads get closer to you with each “Aha!” moment they have.
What is the Difference Between Enterprise Sales and SMB Sales?
When it comes to the Product-Led Growth (PLG) funnel in selling to SMBs versus enterprises, significant differences emerge in the approach and effectiveness of the strategy.
Through our recent interactions with industry experts, a common sentiment emerged: “As you move up the company size spectrum, the traditional self-serve buyer’s journey starts to diminish in its effectiveness.”
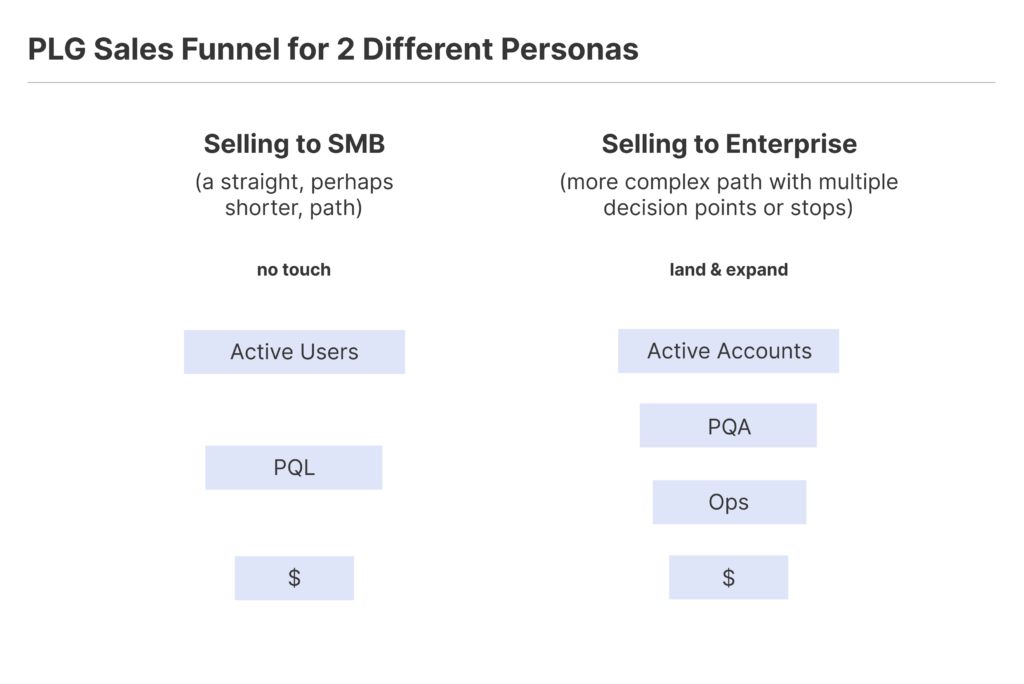
For SMBs:
- Product–qualified leads (PQLs) are at the heart of the sales approach. SMBs, typically having a more straightforward decision-making process, can be targeted effectively through direct product engagement. This is where a potential buyer or user shows interest or engages with the product, quickly seeing its value.
- These businesses often have a self-serve buying model. In this scenario, individual leads play a pivotal role as SMBs can rapidly assess and see the value in products, especially in the SaaS context.
For Enterprises:
- A straightforward PLG approach that solely focuses on individual leads becomes ineffective. Given the intricacies of enterprise-level companies, the strategy must shift from individual leads to an account-centric approach.
- This transition emphasizes Product-qualified accounts (PQAs), focusing on the broader company engagement rather than zeroing in on individual “hand-raisers”. Even though these hand-raisers (individual potential buyers or users) are crucial, they are just one piece of a larger puzzle when dealing with enterprises.
- Enterprises comprise multiple decision-makers and influencers. The PLG sales strategy, in this context, must holistically engage the entire account, fostering relationships with all stakeholders involved. This involves understanding the company’s broader needs, and challenges, and aligning the product’s value proposition accordingly.
4 Types of Product-led Growth Funnel
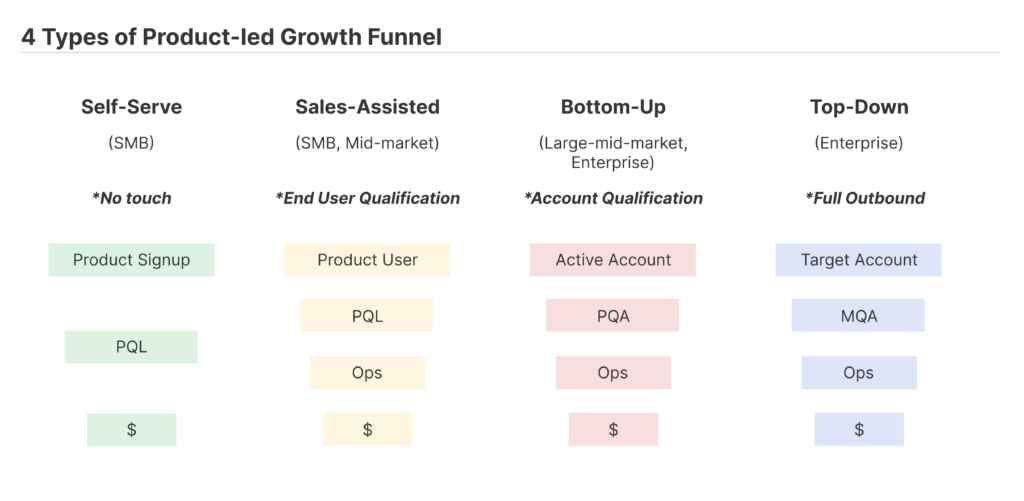
There are four types of PLG funnels for different PLG companies: self-serve, sales-assisted, bottom-up, and top-down. Each business has its own process, target audience, and goals, so some funnels are more useful than others.
For example, the most common type of funnel in micro-saas is the self-serve funnel, which doesn’t need sales or support to understand and start using the product.
1. Self-Serve Funnel
Funnel Progression: Product Signup → PQL → Revenue
The self-serve funnel is characterized by its high volume of users but typically contributes less to the overall sales pipeline. Here, individual users onboard themselves, exploring the product until they perceive enough value to make a purchase.
It is most relevant in industries or contexts where individual users can easily make buying decisions without going through layers of approval. However, in regulated industries like banking, this funnel is less common due to regulatory constraints.
Data for this funnel is centralized in a data warehouse, where detailed cohort reports are generated to pinpoint any bottlenecks in the onboarding process, enhancing the user experience further.
What can be offered:
- In-product tutorials and walkthroughs
- Self-help resources such as FAQs and user forums
- Limited-time premium feature trials
How to identify users at this stage:
- Track user sign-ups and the completion of onboarding tasks.
- Monitor users who consistently access premium trial features.
- Identify users who upgrade to paid plans from within the product.
2. Sales-Assisted Funnel
Funnel Progression: Product User → PQL → OPS → Revenue
In the sales-assisted funnel, there’s a synergy between product use and the sales team. Sales reps engage with users who show significant activity on the product, guiding them towards making a purchase.
This funnel is prevalent in many PLG companies where the emphasis is on complementing the user’s product experience with timely assistance and white-glove onboarding if necessary.
Since salespeople play a pivotal role here, the user and engagement data is typically presented within a CRM system, allowing for tailored outreach campaigns.
What can be offered:
- Personalized demos and product training
- Direct communication channels with sales reps
- Exclusive promotions or discounts for high-engagement users
How to identify users at this stage:
- Identify users with high activity or those who repeatedly access advanced features.
- Track users who engage with sales outreach or attend product webinars.
- Monitor conversions from demos or interactions with sales reps.
3. Bottom-Up Funnel
Funnel Progression: Account Active → PQA → OPS → Revenue
This funnel strategy focuses on broader account-level activity, transcending individual user actions. It’s about understanding the collective engagement of an account with the product.
It’s ideal for situations where one active user from a large account, say Facebook, doesn’t necessarily signify that the entire account is ready to make a large-scale purchase.
This complex funnel requires detailed analytical tools. Many companies utilize dashboards, such as those in UserMotion, to visualize accounts by active users within a specific timeframe, empowering reps to target the most engaged accounts.
What can be offered:
- Team or department-wide product training sessions
- Volume or tier-based pricing discounts
- Account-level analytics and reporting
How to identify users at this stage:
- Monitor overall account activity, including active users and feature utilization.
- Track accounts that request or attend group training sessions.
- Identify accounts that inquire about volume or tier-based pricing.
4. Top-Down or ABM Funnel
Funnel Progression: Target Account → MQA → OPS → Revenue
This approach involves cherry-picking target accounts and strategically identifying the right stakeholders within those accounts for outreach.
It’s suitable for businesses that clearly understand their high-value target accounts and prefer a tailored marketing approach for each.
Many companies deploy separate Account-Based Marketing (ABM) solutions to drive these campaigns. However, integrating data from the bottom-up funnel with these solutions often presents challenges.
What can be offered:
- Customized product presentations tailored to target account needs
- Exclusive pilot programs or early access to new features
- Strategic partnerships or integration support
How to identify users at this stage:
- Track engagement of predefined target accounts with marketing campaigns.
- Monitor feedback or inquiries from these accounts.
- Identify accounts that express interest in partnerships or integrations.
What is a Product-led Growth Flywheel?
A product-led growth flywheel is a framework built around improving the user experience to get more customers.
Its main goal is to boost business sales and growth. By taking advantage of what users do, this method efficiently grows the number of customers while trying to lower the cost of getting new customers.
This flywheel works by making users happier, which makes them more likely to tell others about it and has a compounding effect on getting new users.
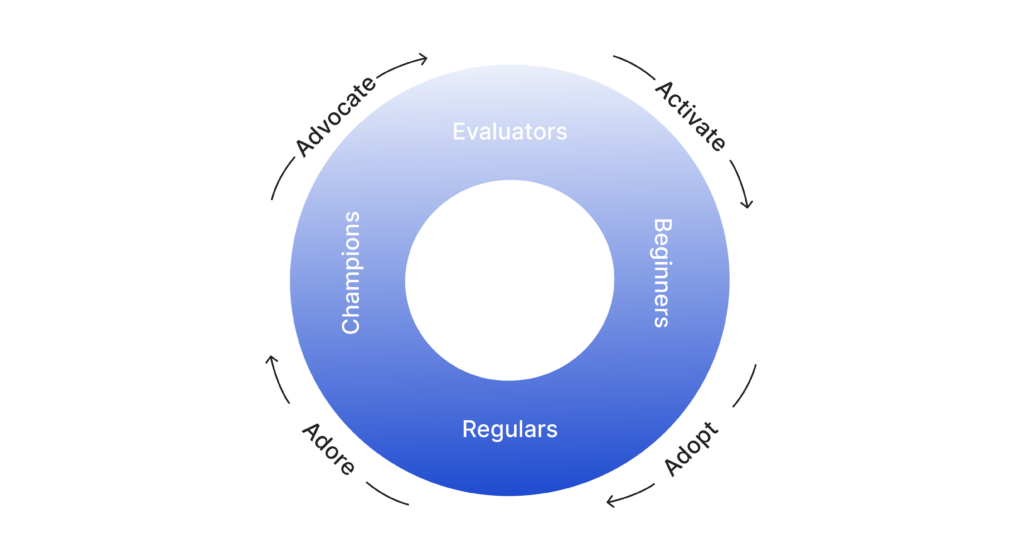
The PLG Flywheel is structured in two main sections:
- User Segments
- Evaluators: Users who are in the phase of trying or testing out the product.
- Beginners: Individuals who consistently use the product, having moved past the initial stages.
- Regulars: Frequent users who have integrated the product into their regular activities.
- Champions: Loyal users who utilize the product and actively promote and endorse it to others.
- User Actions
- Activate: Here, users transition into regular users, integrating the product into their routine.
- Adopt: Users enhance their usage, diving deeper into the product’s functionalities.
- Adore: This entails broadening the scope of product usage or understanding.
- Advocate: Loyal users recommend the product to their network, further propelling the flywheel’s momentum.
Evaluate: Evaluators to Beginners
The evaluation stage is crucial as it offers the first touchpoint between the user and your product. Users looking for solutions to their challenges aim to derive value from your product. It’s essential that this initial interaction is positive, giving the user ample freedom to explore your product’s features.
Remember, it’s always better to give before asking. Therefore, your product should provide value before requesting details such as credit card information.
For instance, offering a free trial or freemium account can be an effective way to showcase your product’s capabilities, allowing users to evaluate its suitability.
What can be offered during the Evaluation stage?
- Free Trial
- Sandbox Project/Test Environment
- In-App Messaging
- Basic Walkthroughs
- “Book Demo” Option
- Video Overview
- Transparent Pricing and Features
- Option to Extend Trial up to 5 Days
How to identify a user in the Evaluation stage?
- Monitor data related to initiating free trials and test environments.
- Observe data regarding user onboarding duration and completion.
- Analyze user activity.
- Examine user conversation metrics.
Adopt: Beginners to Regulars
The adoption phase is marked by the user’s realization of your product’s potential solution to their needs. This awareness arises when they discern your product’s value and delve deeper into its features.
In the Product-Led Growth (PLG) sales funnel, emphasizing user actions on the product is pivotal to drive adoption. Observing value in specific functionalities can guide a user’s choices.
Track product interactions that can indicate imminent adoption.
Once an activation event is noted, strategize on converting that engagement into revenue.
What can be offered during the Activation stage?
- Gamification Features
- Tool Tips
- Best Practices Guides
- Timed Subscribe Modals
- Transparent Pricing and Features
How to identify a user in the Activation stage?
- Track product interactions and identify activation events.
- Study product analytics.
- Engage in customer interviews.
Adore: Regulars to Champs
The adoration stage in the PLG funnel follows adoption. Here, it’s recognized that the user dedicates more time to the product.
What can be offered during the adoration stage?
- Use Case Demonstrations
- Best Practices Guides
- Playbooks
- Templates
How to identify a user in the adoration stage?
- Understand if they’re integrating your product into their regular workflows.
- Track user data to ascertain genuine data usage and results derivation.
- Review interactions with the test environment.
Champs
The Champs stage is where user engagement and satisfaction are at their highest. At this point, users have not only made your product a big part of their daily lives, but they are also actively promoting it and acting as brand ambassadors.
Their dedication is shown by how often they use the site, how much they participate in community discussions, and how eager they are to tell others about the good things that have happened to them.
What can be offered to a user in the Champs stage?
- Advanced customization options
- Exclusive access to beta features
- Opportunities to be featured in case studies
- Loyalty rewards or discounts
- Invitations to user advisory boards or feedback panels
How to identify a user in the Champs stage?
- Monitor their advocacy and referrals of new users.
- Track their active participation in community discussions or forums.
- Engage directly, observing their enthusiasm and eagerness to share success stories.
- Review feedback and suggestions they offer, indicating a deep understanding and vested interest in your product.
Key Takeaways
💡 After all, we have discussed what PLG means, what are a PLG funnel and the stages in the Product-Led-Growth (PLG) sales funnel.
💡Product Led Growth (PLG) is a business strategy that puts your product in the front.
💡 PLG uses the product itself to acquire, retain, and expand customers and puts the product in front of marketing and sales activities.
💡 PLG funnel includes four stages: evaluation, activation, initiation, and adoption, with different strategies and metrics for each stage.
💡 The PLG funnel describes users as evaluators, beginners, regulars, and champs, in different stages.
You can get more information about best practices and user behaviors here on PLG Sales Funnel – Best Practices Notion page!
FAQ
What does PLG mean in sales?
What are the 3 parts of the purchase funnel?
The purchase funnel consists of three parts, which are the top of the funnel: awareness, the middle of the funnel: consideration, and the bottom of the funnel: conversion.