In sales and marketing, the terms “signal-based selling” and “lead-scoring” often come up. But are they really different? Some argue that signal-based selling is just a rebranded version of lead-scoring. Let’s dive into this debate.
What is Signal-based Selling?
Signal-based selling is a modern sales approach that involves monitoring and analyzing various signals from potential customers to guide sales efforts. (We have more about signal based selling in our previous article → What is Signal-based Selling?). These signals include:
- Online Behavior: Actions taken on the internet, such as website visits, clicks, and social media interactions that show intent data.
- Social Behavior: Engagement on social platforms, including likes, shares, and comments.
- Website Activity: Specific behaviors on a company’s website, like time spent on pages, downloads, and form submissions.
- Downloads: Content downloads, such as whitepapers, e-books, and case studies.
- Job Changes: Career moves and role changes, which can indicate new opportunities for sales.
This method focuses on continuous engagement and collecting data both before and after initial meetings, aiming to maintain a comprehensive view of the customer’s journey.
What is Lead Scoring?
Lead scoring is a method used to rank prospects against a scale that represents the perceived value each lead represents to the organization. Points are assigned based on various attributes and behaviors, such as:
- Demographic Information: Age, job title, industry, company size.
- Behavioral Data: Website visits, email opens, content downloads.
- Engagement Levels: Interaction with marketing campaigns, frequency of visits, social media activity.
The primary goal is to prioritize leads based on their likelihood to convert into customers, thus enabling sales teams to focus their efforts on the most promising prospects.
Difference Between Signal-based Selling and Lead Scoring
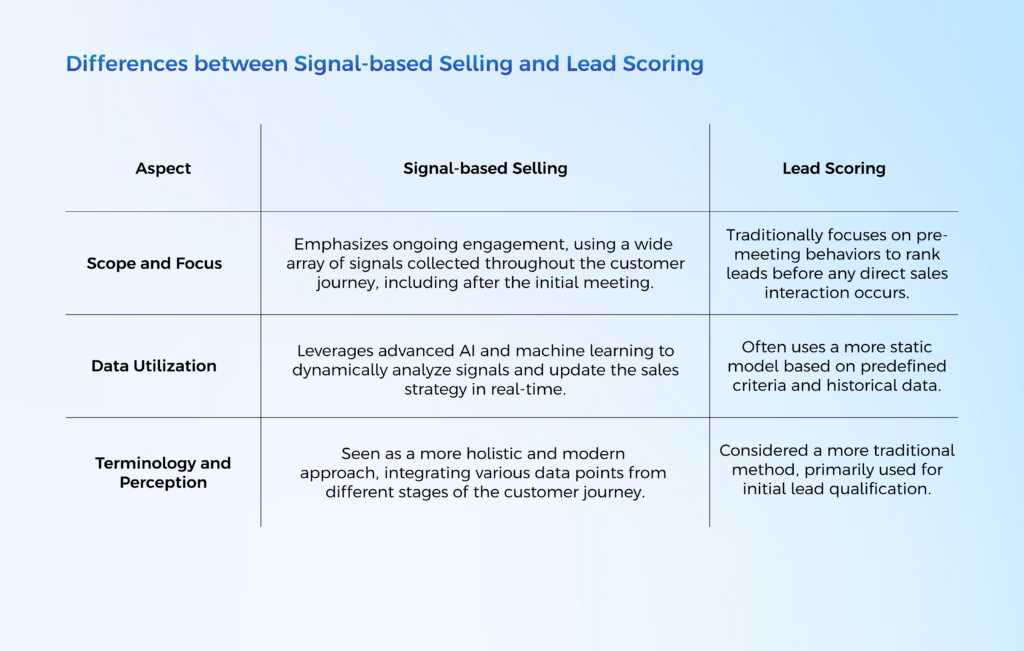
Scope and Focus
Signal-based Selling emphasizes ongoing engagement, using a wide array of signals collected throughout the customer journey, including after the initial meeting.
By analyzing data from each stage, the team can provide personalized follow-ups and maintain engagement, increasing the chances of upselling or securing repeat business.
Lead Scoring traditionally focuses on pre-meeting behaviors to rank leads before any direct sales interaction occurs.
The sales team then prioritizes these leads for outreach, aiming to convert the highest-scoring leads into customers quickly.
Data Utilization
Signal-based Selling leverages advanced AI and machine learning to dynamically analyze signals and update the sales strategy in real-time.
If the AI detects a pattern indicating high purchase intent, it could notify the sales team to take immediate action, such as sending a personalized offer.
Lead Scoring often uses a more static model based on predefined criteria and historical data.
A static lead scoring model might assign points to leads based on specific actions, such as attending a webinar (10 points) or requesting a demo (20 points). Leads with the highest scores are deemed most likely to convert and are prioritized for follow-up.
Terminology and Perception
Signal-based Selling seen as a more holistic and modern approach, integrating various data points from different stages of the customer journey.
For example, a company might promote its use of signal-based selling to highlight its commitment to sales techniques and its ability to adapt to changing customer behaviors.
Lead Scoring considered a more traditional method, primarily used for initial lead qualification.
It is viewed as a tried-and-true method. A company might emphasize its lead scoring process to demonstrate its systematic approach to prioritizing leads and its reliance on proven methodologies to drive sales.
Similarities Between Signal-based Selling and Lead Scoring
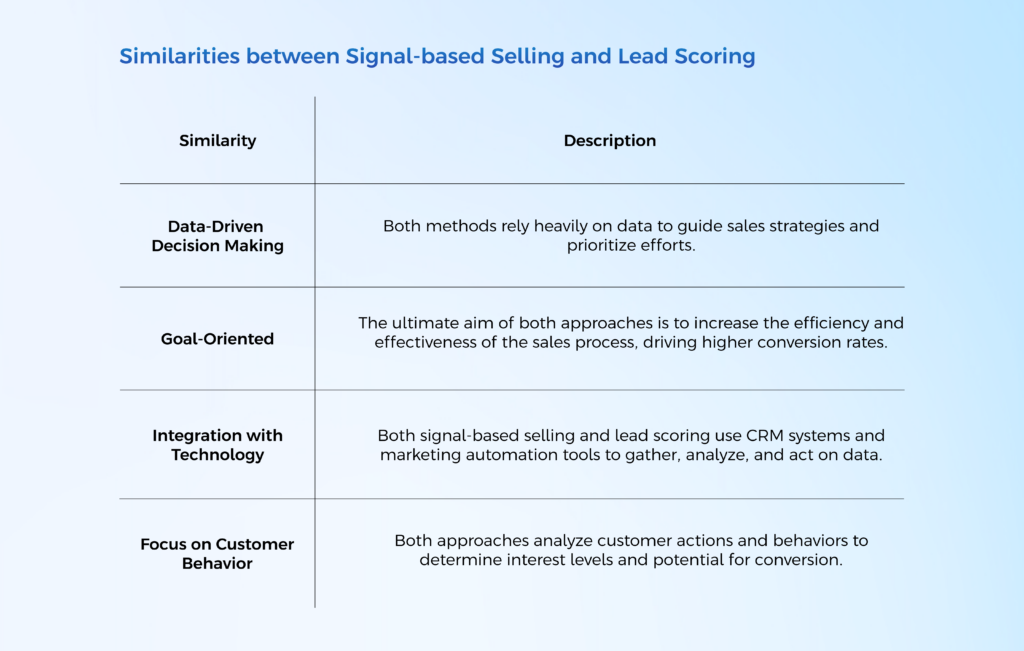
Data-Driven Decision Making
Both signal-based selling and lead scoring rely heavily on data to guide sales strategies and prioritize efforts.
In practice, this means that sales teams are not relying on gut feelings or anecdotal evidence to make decisions. Instead, they use concrete data points to inform their actions.
For example, a company might track how often a lead visits their website, interacts with their emails, or engages on social media.
This data helps sales teams understand which leads are more likely to convert into customers.
By analyzing these data points, companies can create targeted strategies that address the specific needs and behaviors of their prospects, leading to more efficient and effective sales processes.
Goal-Oriented
The ultimate aim of both signal-based selling and lead scoring is to increase the efficiency and effectiveness of the sales process, driving higher conversion rates.
This goal-oriented approach ensures that both methods are focused on delivering tangible results.
For instance, a sales team might use lead scoring to identify the highest-potential leads and prioritize their efforts on those individuals, thereby increasing the likelihood of closing deals.
Similarly, signal-based selling might involve monitoring post-meeting engagement to nurture relationships and move prospects further down the sales funnel.
By aligning their strategies with clear, measurable goals, both methods help sales teams work smarter, not harder, ultimately boosting revenue and growth.
Integration with Technology
Both signal-based selling and lead scoring use CRM systems and marketing automation tools to gather, analyze, and act on data.
These technologies play a crucial role in implementing both methods effectively.
For example, CRM systems like Salesforce or HubSpot allow sales teams to track every interaction with a lead, from initial contact to final sale. Marketing automation tools like Marketo or Pardot can automate the process of scoring leads based on their behavior and engagement levels.
By integrating these technologies, companies can ensure that their sales processes are seamless and data-driven, enabling them to respond quickly to changing customer behaviors and market conditions.
Focus on Customer Behavior
Both approaches analyze customer actions and behaviors to determine interest levels and potential for conversion.
This focus on customer behavior is at the heart of both signal-based selling and lead scoring.
For example, a company might analyze which blog posts a lead has read, what webinars they’ve attended, or which products they’ve viewed on their website.
By understanding these behaviors, sales teams can gain insights into what the lead is interested in and tailor their approach accordingly.
This might involve sending personalized content, offering relevant product recommendations, or scheduling follow-up meetings to address specific questions or concerns.
By focusing on customer behavior, both methods help sales teams build stronger relationships with their prospects and increase the likelihood of conversion.
Supporters of Signal-Based Selling Say
Modern Evolution
Signal-based selling has evolved from traditional lead-scoring by incorporating a broader range of signals. These include online behavior, social interactions, website activity, downloads, and job changes.
Post-Meeting Focus
True sales signals, they argue, occur after the initial meeting. This approach emphasizes ongoing engagement and behavioral cues that happen during the sales process, rather than just before a lead is contacted.
Enhanced Data Utilization
Today’s signal-based models use advanced AI and machine learning to create more sophisticated and dynamic scoring systems, far beyond the static models of the past.
Critics Argue
Rebranding Without Substance
Critics claim that signal-based selling is essentially the same as lead-scoring, just with a new name. All the signals used in signal-based selling have been part of lead-scoring models for years.
Pre-Meeting Signals Matter
They argue that significant insights can be gleaned before any initial meeting, and these pre-meeting signals are crucial for a comprehensive understanding of a lead’s intent and interest.
Database Changes
The distinction between opted-in contacts and non-opted-in contacts has blurred. Modern CRMs often contain a mix of both, making traditional lead-scoring methods still relevant and effective.
Open for Debate
Does signal-based selling represent a true innovation in sales strategy, or is it merely a new label for the same old practices?
57% says that signal based selling should be included in a lead-scoring model. They say it is like lead-scoring’s modern cousin, but with a focus on what happens after the initial meeting.
26% also considers that signal-based selling is just ABM with a new name.
Some supports that the diversity of signals available today makes it vastly different from the leader scoring of yesterday.
Finally, we also hear some criticism that lead scoring is only valid when the person is actually inbound. This is the purpose of understanding the signals before this happens.
Personal Thoughts
In my view, signal-based selling is very similar to, and almost the same thing as, lead scoring and even account-based marketing (ABM). It represents an evolved version of these traditional methods.
While signal-based selling may appear more modern by incorporating advanced AI and machine learning to analyze a wide array of signals throughout the customer journey, the core principles remain consistent with lead scoring.
Both approaches aim to use data-driven insights to prioritize and guide sales efforts, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of the sales process.
Signal-based selling can be seen as an advanced iteration of lead scoring, leveraging more technologies and a broader range of signals.
Similarly, account-based marketing shares this data-driven focus but extends it to target specific accounts rather than individual leads.
Ultimately, the distinctions between these methods lie in their scope and technological integration, but their fundamental objectives and reliance on data are closely aligned.